Factors Influencing Average KWh Usage
-_FI.png)
The average kilowatt-hour (kWh) usage in a 2-bedroom apartment is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including appliance usage, occupancy, lifestyle choices, and building characteristics. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing energy consumption and reducing electricity bills.
Appliance Usage
Appliance usage is a primary driver of energy consumption in apartments. The energy demands of different appliances vary significantly. For instance, heating and cooling systems are major energy consumers, especially in climates with extreme temperatures.
- Heating and Cooling: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems account for a substantial portion of energy usage, particularly in colder or warmer climates. The size and efficiency of the HVAC system, as well as the thermostat settings, significantly impact energy consumption. For example, a larger apartment with a less efficient HVAC system will generally consume more energy than a smaller apartment with a more efficient system.
- Lighting: Lighting is another significant contributor to energy usage. Traditional incandescent bulbs consume more energy than energy-efficient alternatives such as LED bulbs. Replacing incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs can significantly reduce electricity consumption. For example, switching from a 60-watt incandescent bulb to a 10-watt LED bulb can save approximately 80% of energy.
- Electronics: Electronic devices such as televisions, computers, and gaming consoles also contribute to energy consumption. While these devices may not consume as much energy as heating or cooling systems, their cumulative energy usage can be substantial, especially if left on standby mode. Unplugging electronic devices when not in use can help reduce energy consumption. For example, a typical television consumes about 100 watts of power when in use and around 5 watts in standby mode. Leaving a television in standby mode for 24 hours can consume 120 watt-hours of energy, equivalent to running a 60-watt light bulb for 2 hours.
Occupancy and Lifestyle Choices
The number of occupants in an apartment and their lifestyle choices significantly impact energy consumption.
- Occupancy: A larger number of occupants generally translates to higher energy consumption due to increased use of appliances and lighting. For example, a family of four will likely use more energy than a single person living in the same apartment.
- Lifestyle Choices: Lifestyle choices such as showering habits, laundry frequency, and cooking methods can significantly impact energy consumption. For instance, taking shorter showers and using energy-efficient appliances like washing machines and dishwashers can help reduce energy consumption.
Building Insulation and Design
Building insulation and design play a crucial role in energy efficiency and KWh usage.
- Insulation: Proper insulation helps prevent heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, reducing the workload on HVAC systems and energy consumption. For example, a well-insulated apartment with double-paned windows can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 20% compared to an apartment with poor insulation and single-paned windows.
- Window Efficiency: Windows are a major source of heat loss and gain. Double-paned windows with low-emissivity coatings are more energy-efficient than single-paned windows, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
- Building Design: The design of the apartment building, including its orientation, shading, and ventilation, can also impact energy consumption. For example, apartments with south-facing windows receive more sunlight, reducing the need for artificial lighting and heating.
Typical KWh Usage Ranges
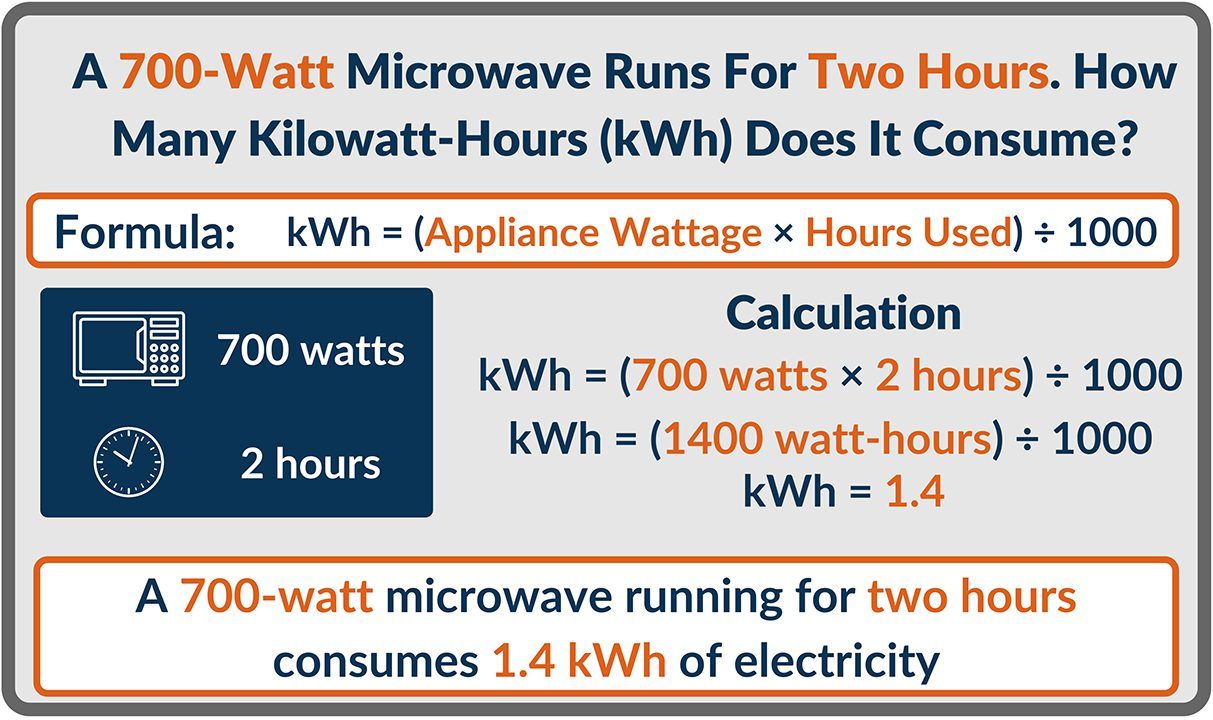
Understanding the typical KWh usage ranges for a 2-bedroom apartment can help you estimate your energy consumption and identify areas for potential savings. The average KWh usage can vary significantly depending on factors such as location, climate, household size, and energy-efficient practices.
Average KWh Usage Ranges by Region/Climate, Average kwh usage 2 bedroom apartment
The following table provides a breakdown of typical KWh usage ranges for a 2-bedroom apartment in different regions or climates. The ranges are based on average household consumption and may vary depending on individual usage patterns.
| Region/Climate | Average KWh Usage (Low) | Average KWh Usage (Medium) | Average KWh Usage (High) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperate Climate (e.g., Seattle, Washington) | 500-700 KWh | 700-900 KWh | 900-1100 KWh |
| Hot Climate (e.g., Phoenix, Arizona) | 700-900 KWh | 900-1100 KWh | 1100-1300 KWh |
| Cold Climate (e.g., Chicago, Illinois) | 800-1000 KWh | 1000-1200 KWh | 1200-1400 KWh |
Energy-Efficient Practices for Lower KWh Usage
There are numerous energy-efficient practices that can contribute to lower KWh usage within each range. Here are some examples:
* Temperate Climate:
* Insulation: Ensure proper insulation in your apartment to minimize heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
* Energy-efficient appliances: Replace older appliances with energy-efficient models.
* LED Lighting: Switch to LED bulbs, which consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs.
* Hot Climate:
* Shade: Utilize blinds, curtains, or awnings to block direct sunlight and reduce heat gain.
* Ceiling Fans: Install ceiling fans to circulate air and provide cooling relief.
* Efficient AC System: Ensure your air conditioning system is properly maintained and operates efficiently.
* Cold Climate:
* Programmable Thermostat: Use a programmable thermostat to adjust the temperature based on your schedule and reduce heating costs.
* Weather Stripping: Seal windows and doors with weather stripping to prevent drafts and heat loss.
* Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in your apartment to prevent moisture buildup and improve indoor air quality.
Reducing KWh Usage: Average Kwh Usage 2 Bedroom Apartment
Lowering your electricity consumption in a 2-bedroom apartment can significantly reduce your energy bill and environmental impact. This can be achieved through a combination of smart practices, efficient appliances, and mindful energy habits.
Energy-Efficient Appliances and Lighting
Choosing energy-efficient appliances and lighting can significantly reduce your electricity consumption. Energy Star-rated appliances, for example, are designed to use less energy while maintaining optimal performance.
- Refrigerators: Modern refrigerators with Energy Star ratings use less energy than older models. Consider a refrigerator with an automatic ice maker, as it uses less energy than a manual one.
- Dishwashers: Energy Star-rated dishwashers use less water and energy than older models. They also often have features that optimize water usage, such as sensors that detect the level of soiling.
- Washing Machines and Dryers: Energy Star-rated washing machines and dryers use less water and energy than older models. They often have features that reduce water and energy usage, such as a “cold wash” setting or a “sensor dry” function.
- Lighting: LED bulbs use significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs. They also last much longer, reducing the need to replace them frequently.
Adjusting Thermostat Settings
Thermostat settings play a crucial role in your energy consumption. By adjusting your thermostat settings, you can significantly reduce your energy bill.
- Lowering Thermostat in Winter: Lowering your thermostat by just a few degrees during the winter can save a significant amount of energy. Consider setting your thermostat to 68 degrees Fahrenheit during the day and 65 degrees Fahrenheit at night.
- Raising Thermostat in Summer: Raising your thermostat by a few degrees during the summer can also save energy. Consider setting your thermostat to 78 degrees Fahrenheit during the day and 75 degrees Fahrenheit at night.
- Utilizing Programmable Thermostats: Programmable thermostats can automatically adjust your thermostat settings based on your schedule, further reducing your energy consumption.
Utilizing Smart Home Technology
Smart home technology can be a valuable tool for reducing your energy consumption. Smart thermostats, for example, can learn your heating and cooling preferences and adjust your thermostat settings accordingly.
- Smart Plugs: Smart plugs allow you to monitor and control the power consumption of your devices. You can use them to turn off devices that are not in use, such as lamps or TVs.
- Smart Appliances: Some appliances, such as refrigerators and washing machines, are now available with smart features that allow you to control them remotely and monitor their energy consumption.
Visual Representation of Impact
Average kwh usage 2 bedroom apartment – The impact of implementing energy-saving measures can be visualized through a chart or infographic. For example, a chart could depict the percentage reduction in energy consumption for each measure implemented. The chart could show that switching to LED bulbs can reduce lighting energy consumption by 75%, while using a programmable thermostat can reduce heating and cooling energy consumption by 10-15%.
The average 2-bedroom apartment uses around 1,000 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per month, but that can vary depending on factors like climate, appliance usage, and even the size of the apartment. If you’re looking for a luxurious escape, consider booking a stay at the mandalay bay panoramic 2 bedroom suite , which might use a bit more energy thanks to its amenities.
But hey, a little extra energy usage is worth it for a vacation, right?
The average 2-bedroom apartment uses around 1,000 kWh per month, but that can vary depending on factors like climate, appliance usage, and even the efficiency of the building itself. If you’re looking for a new place in Arkansas, check out the 2 bedroom apartments conway ar listings to find a cozy and efficient home.
Understanding your average kWh usage can help you budget for your energy costs and make informed decisions about your energy consumption.
